For the most part, penis anatomy is quite straightforward.
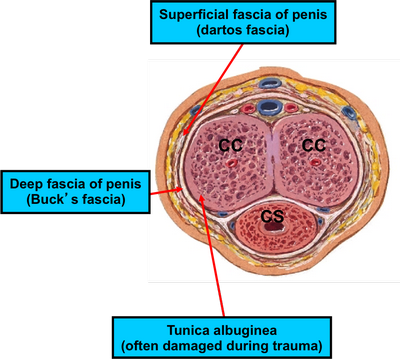
The basic structure of the penis is the corpora cavernosa, which is the base of the penis, along with the corpus spongiosum which is the bulbous part that hangs out of the corpora cavernosa. The next major structure in the body that is important when thinking about the anatomy of a penis is the paired corpora bulbosa, which is the spongy structure at the top of the penis.
As illustrated in this diagram showing the basic penile anatomy, the key structures in the important erectile tissue that make up the erect penis are the corpora cavernosa and the corpora bulbs, which both contribute to the overall penile anatomy when considering the penis anatomy. Of the two, the corpora bulbosa is by far the thicker one and makes up the most important part of the penis when it comes to penis anatomy.
Penis size is also determined by the penis anatomy. The length of the penis is largely determined by the length of the corpora cavernosa, as it determines the length of the shaft that extends from the corpora cavernosa to the tip of the erect penis. In terms of the thickness, the corpora bulbosa is much thinner than the corpora cavernosa and hence determines the thickness of the erect penis.
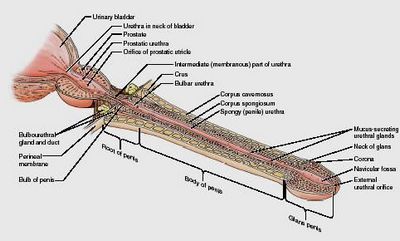
As a result, the erect penis that reaches the top of the pubic region will not be as thick as a penis that has a thicker penis anatomy. Penis size also depends on the thickness of the erect penis and the size and girth of the erect penis as well.
When considering the erection of the erect penis, both the corpora cavernosa and the corpora bulbs make up the erect penis, and hence the erect penis anatomy. The erect penis is composed of both the corpora cavernosa and the corpora bulbs and the erection of these structures determine the quality of the erection.
Since the erect penis consists of both the corpora cavernosa and the corpora bulbs, which are part of the erect penis anatomy, these structures need to be held together by ligaments or tissues called ligaments of the corpus spongiosum. These tissues form the basis of the erect penis anatomy and they are responsible for holding the erect penis erect penile tissues together. This penile tissue is important to the erect penis because the ligaments hold the erect penis erect in a semi-erect position during an erection.
The erect penis is held in this semi-erect position by the ligaments of the corpus spongiosum.
When looking at the erect penis, it is important to remember that the corpus spongiosum and the corpora bulbosa also make up the erect penis. The corpus spongiosum is a thin ligament that goes from the head of the penis to the base of the erect penis and provides a firm support for the erect penis when erecting. Similarly, the corpora bulbosa is a thick spongy tissue that holds the erect penis in place when erecting.
After the corpus spongiosum, there are two more structures that come into play for the erect penis; these structures are the corpus spongiosum arterioles. These arteries connect the corpus spongiosum to the corpora bulbs and the corpus spongiosum venules. These venues are the structures that help to dilate the corpora cavernosa, and the corpora bulbosa together form the corpora cavernosa arterioles.
The penile spongiosum arterioles and the corpora spongiosum arterioles are the structures that make up the erect penis and their function is to dilate the corpora cavernosa when erect and when the erect penis becomes hard. These two structures also make up the erect penis anatomy and these structures form the erect penis anatomy.
Leave a Reply