This is the main type of ischemic stroke.
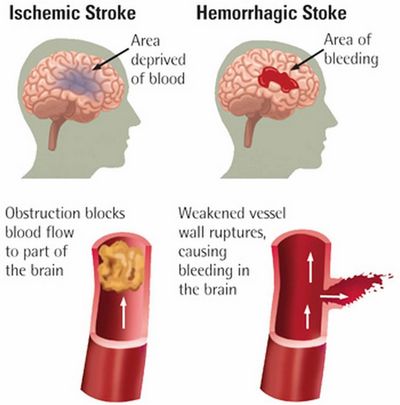
In this type of ischemic stroke, there is blockage (caused by aneurysm) in the artery that supplies blood to the brain (drainage in a part of the artery). In many cases, the clot forms in a part of the artery in the neck (a carotid or vertebral artery) that runs to the left side of the head, where the brainstem functions. At other times, the clot forms in a deep vein, like a vein that runs down the leg. As it travels to the brainstem, it may cause a transient ischemic attack (TIA), which is sudden headache, dizziness, numbness, disorientation and a feeling of faintness.
Cerebral thrombosis (or plastic stroke) This type of ischemic stroke occurs due to lack of blood supply to an artery that supplies blood to the cerebral cortex. Plasmic ischemic strokes occur due to a clot that forms outside the brain and travels to the limb or brain.
This type of ischemic stroke usually requires medical treatment for a period of time; however, it will eventually subside on its own and is not fatal.
Intravenous insufficiency This is a type of ischemic stroke that occurs due to vein infection of the brain or the blood vessels. Although intraparenchymal venous disease is a leading cause of stroke, it can also occur due to blood clots formed by tumors and varicose veins.
Ischemic neuropathy This type of ischemic stroke occurs when a nerve in the body becomes damaged. The symptoms include numbness, pain, weakness and difficulty in moving the extremities. The affected nerve will also become less sensitive to external stimuli and the body’s organs will be unable to use it as it was before. This type of ischemic stroke can be either primary or secondary. primary ischemic neuropathy is caused by damage to the bronchial wall of a spinal cord; secondary ischemic neuropathy is caused by damage to nerves on the level of the central nervous system.
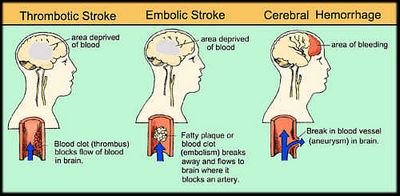
the damage causes nerve signals to be diverted to another part of the body or the brain
Isthmic and subthrombicular ischemic strokes are the subtypes of ischemic strokes. The first subtype is called intraparenchymal. and the second subtype is called subthrombicular. ischemic strokes occur because the affected nerve can be found only in the neck and is not easily visible without a needle or with a light microscope.
The symptoms of ischemic neuropathy include difficulty in chewing, swallowing, talking, swallowing, vision problems, and problems with vision. Some patients may experience nausea, vomiting, fever, diarrhea, abdominal bloating, cramps, muscle spasms, chest pain and weakness in the extremities.
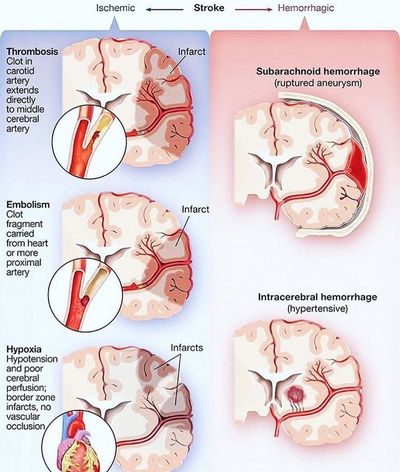
This type of ischemic stroke can be caused by a virus, a chemical reaction, trauma or a blockage in an artery. This type of ischemic stroke is usually treated with medications. The symptoms may recur; however, depending on how severe the injury is, some form of treatment may be required.
This type of ischemic stroke occurs due to injury to the cerebrospinal fluid, causing fluid to accumulate in the skull beneath the skin and surrounding tissues. Cerebral ischemia can result from a traumatic injury or an accident. Sub-arachnoid ischemic stroke is usually caused by a disease like encephalitis or meningitis. This type of ischemic stroke may occur from exposure to head trauma.
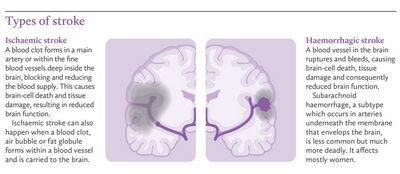
Although it is rare, it can also occur from a tumor. There is no treatment that can prevent this form of ischemic stroke.
These four types of ischemic strokes have important warning signs that can help to detect the condition. Early diagnosis is essential for the recovery of the patient. The signs should prompt medical attention right away. Once the physician is aware that a patient has had one or more of these types of strokes, they may decide to perform further testing to determine if a person has the condition. It is important that patients take care when handling themselves.
Leave a Reply